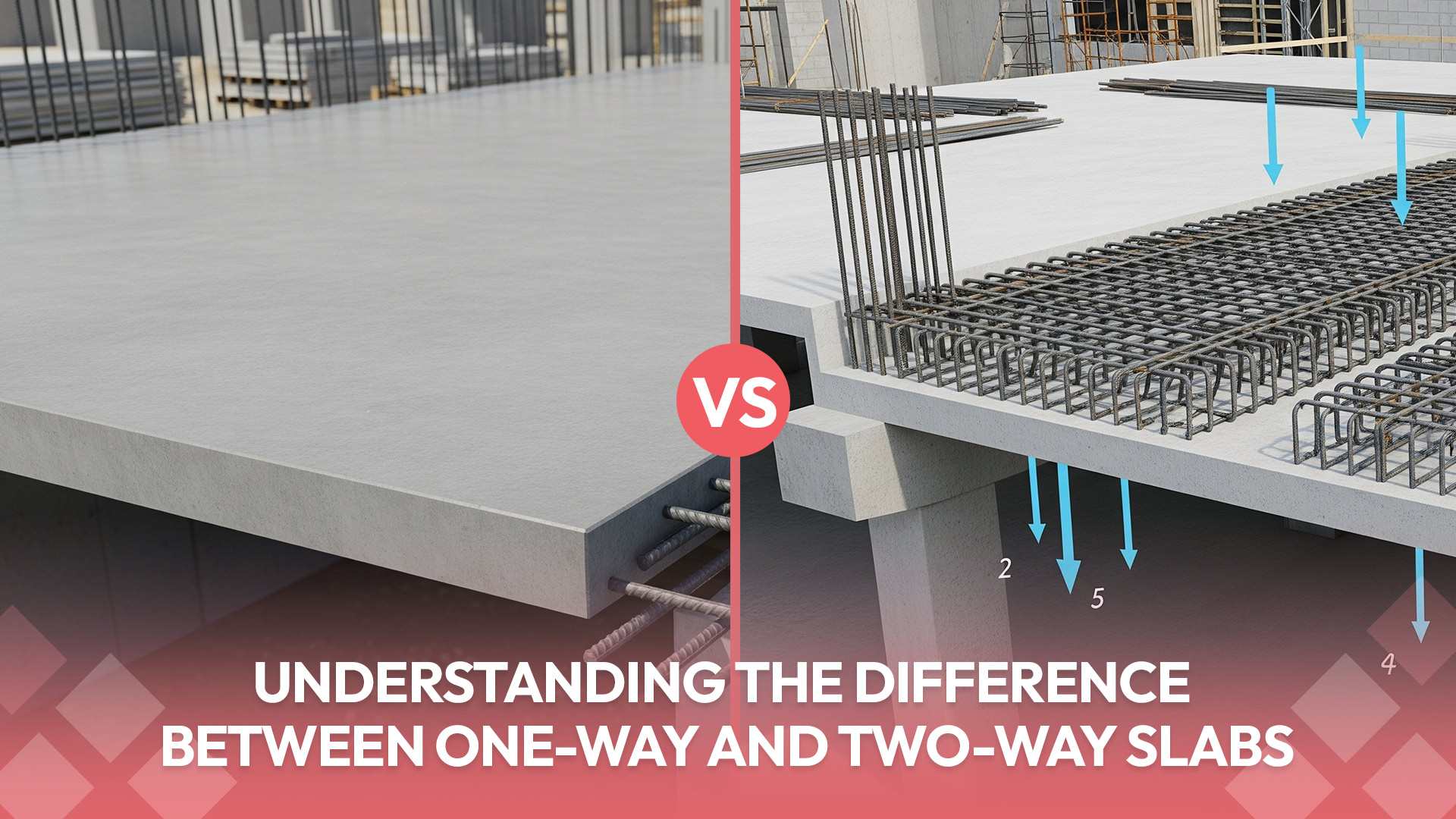
Have you ever wondered why some slabs in construction look and function differently from others? Why does one structure require one type of slab and another structure require a different one? If you’re a civil engineer, an architect, a student, or a professional in the construction industry, understanding the difference between one-way and two-way slabs is essential. These two slab types are not only structural elements but also define the stability, efficiency, and cost of the projects.
This blog will break down the difference between one-way and two-way slabs, looking closely at their construction, applications, and how you can identify and select the right approach for your project. Stick around—we’re going to make this topic simple, clear, and actionable for you.
What Are One-Way Slabs?
One-way slabs are one of the most common structural elements in construction. Think of them like stretched-out beams working in one direction.
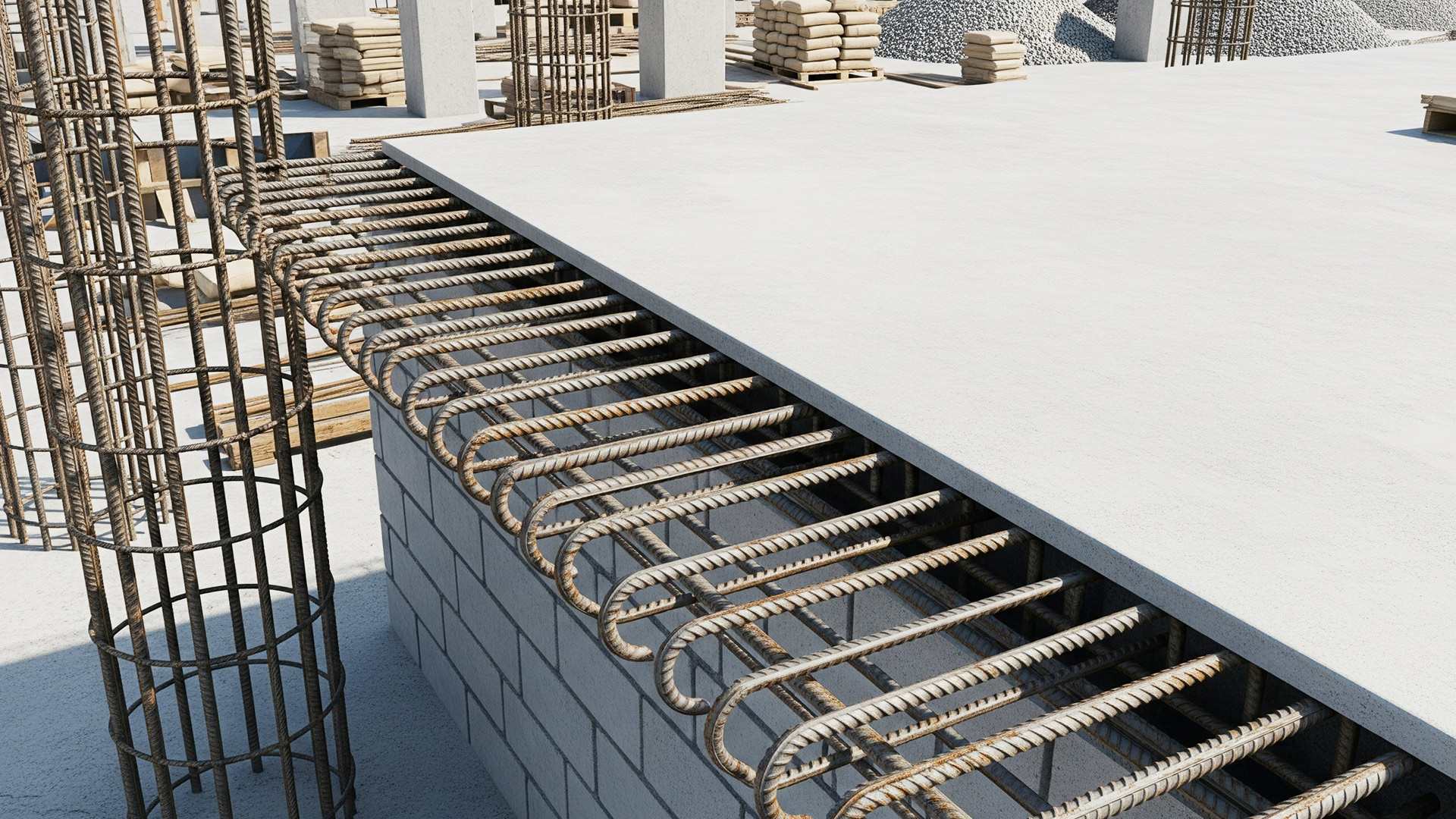
A one-way slab is a reinforced concrete slab where the load is carried in one direction only, either spanning between two parallel beams or walls. These slabs are supported along two opposite edges, and the load transfer mechanism is linear rather than distributed. You’ll frequently see them in narrow hallways, corridors, and small residential spaces where the span runs in one primary direction.
The reinforcement in a one-way slab is provided along the shorter span to resist bending and shear forces. These slabs are relatively simple to design, cost-effective, and quick to construct, making them a go-to option for construction projects with linear spans. Contact us for building construction in Bangalore today!
See Also: Top 5 Modern Trends in Residential Building Design
What Are Two-Way Slabs?
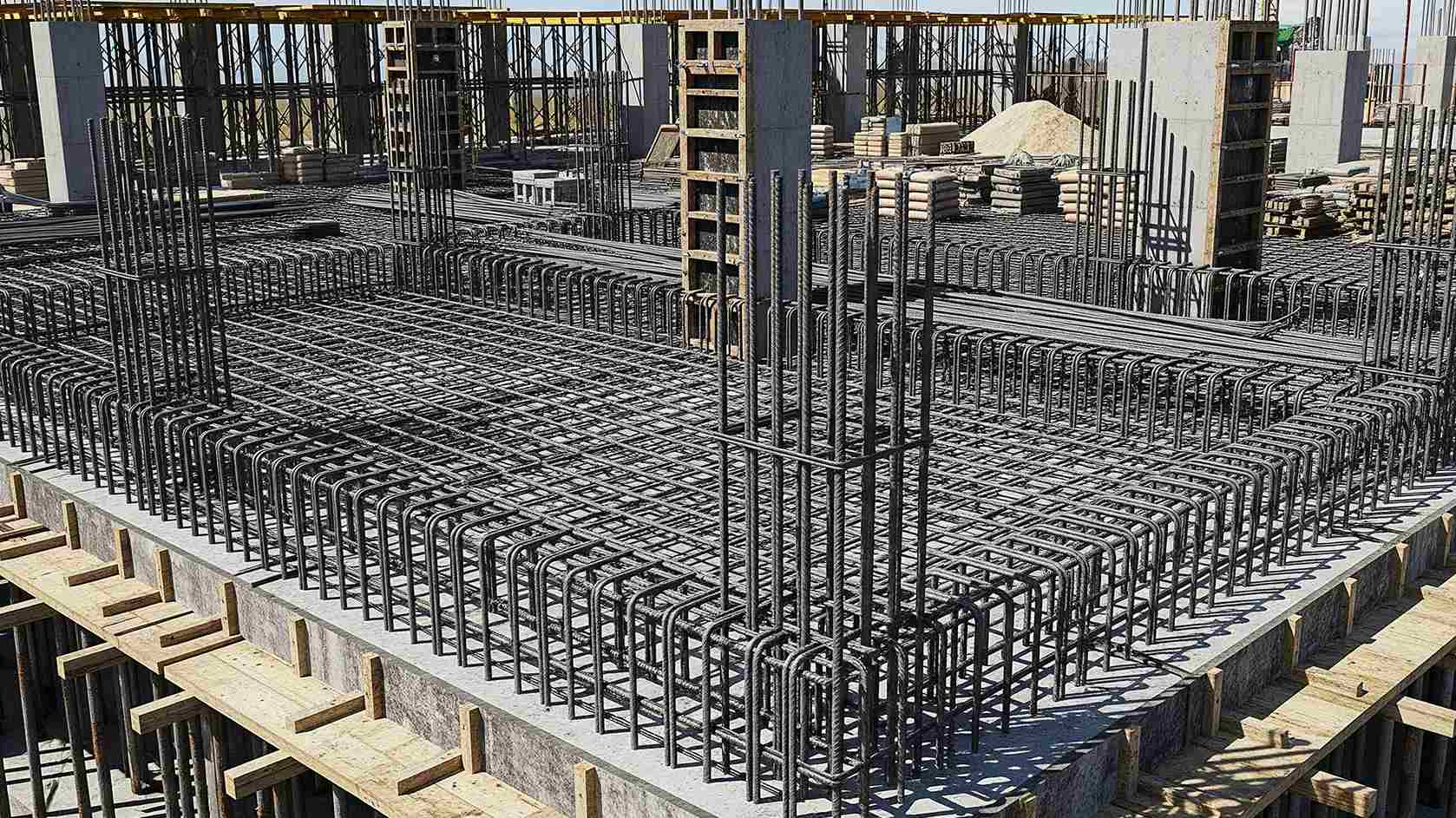
Now, let’s talk about two-way slabs—a more versatile option for larger and more complex structures. Unlike their one-way counterparts, two-way slabs distribute the load in two perpendicular directions. They are supported on all four sides, transferring loads to all connected beams or columns.
Due to their load distribution properties, two-way slabs require reinforcement in both directions to handle bending along both axes. Buildings such as offices, malls, and large public areas often use two-way slabs because of their ability to efficiently manage loads over wide spaces.
While more complex in design and construction compared to one-way slabs, two-way slabs provide better flexibility and strength for projects demanding greater load-carrying capacity.
Difference Between One-Way and Two-Way Slabs
To further simplify the difference between one-way and two-way slabs, let’s break it down into key categories.
1. Direction of Span
The Difference Between One-Way and Two-Way slabs begins with how they handle load transfer. In a one-way slab, the load is carried in a single direction, typically along the shorter span. This makes it suitable for narrower structures.
Conversely, a two-way slab distributes loads in both the shorter and longer directions, providing better load-sharing capabilities. This dual-direction transfer is ideal for structures requiring even weight distribution, such as large public spaces or commercial areas.
Understanding this difference is crucial for structural efficiency and ensuring the slab supports the intended use of the building while meeting engineering requirements.
2. Support
The Difference Between One-Way and Two-Way slabs becomes evident when examining their support systems. One-way slabs are supported by beams or walls on two opposite sides, limiting their load transfer to one direction.
This makes them a practical choice for simpler layouts like residential floors or corridors. On the other hand, two-way slabs are supported on all four sides, allowing them to handle loads in two directions.
This additional support makes two-way slabs better suited for larger spans, like malls or parking lots, where load distribution and structural stability are critical considerations for the design.
3. Load Transfer
Load transfer is another significant Difference Between One-Way and two-way slabs. A one-way slab carries the load in a straight line to two opposite supports, creating a linear load path.
This is effective for simple, narrow structures but limits its use in large areas. Two-way slabs, however, distribute the load evenly across all four supports, ensuring a balanced load transfer in two directions.
This feature makes two-way slabs ideal for larger spaces that require greater structural durability. The choice of load transfer design directly impacts the efficiency and safety of the building, particularly for high-traffic or heavy-load areas.Contact the best construction company in Bangalore today!
4. Thickness
One of the noticeable Differences Between One-Way and Two-Way Slabs is their thickness. One-way slabs are normally slim because load transfer occurs in only one direction, thus easier in terms of material.
It also results in an increased thickness of joists, which in turn makes them a popular option for larger structures such as offices or shopping complexes. The thickness of the slab impacts its load-bearing capability, while its thickness also has an influence on the costs of construction and the use of materials.
5. Reinforcement
The Difference Between One-Way and Two-Way slabs extends to reinforcement placement. In one-way slabs, reinforcement bars are placed only in the shorter span direction to resist bending and support the load.
This focused reinforcement is sufficient for smaller, simpler structures. In two-way slabs, reinforcement bars are laid in both directions, allowing the slab to handle bending and loads along two axes.
This dual reinforcement provides extra strength and stability, making it ideal for wider spans where balanced load distribution is essential. Proper reinforcement placement is critical in ensuring the slab meets safety and structural integrity standards.
See Also: Prefabricated Construction: All You Need to Know
6. Span Length
Span length is a defining Difference Between One-Way and Two-Way slabs. One-way slabs are used for shorter spans where the ratio of the longer span to the shorter span exceeds two. This makes them suitable for long, narrow spaces like hallways or corridors.
Two-way slabs, however, are ideal for wider areas where the ratio of the longer span to the shorter span is less than or equal to two. This adaptability to varying span lengths makes two-way slabs a versatile choice for commercial buildings, offices, and parking structures that require greater coverage and load capacity.
7. Application
The practical Difference Between One-Way and Two-Way Slabs is evident in their applications. One-Way slabs are used in sanitary premises, residential buildings, in the corridors or in all buildings where spans are small and the load is low.
Due to their relatively cheap design and easy construction, they are ideal for use in projects of lower capacities. There is, however, one main difference between one and two-way slabs: two-way slabs are meant for vast areas such as shopping malls, offices or parking lots, as they need to bear more loads.
They are useful in structures which have higher function demand due to their good distribution of weights and their ability to support a lot of traffic. The choice of application has considerable regard for the scope of the project and the structure that needs to be given.
Why Choose TeamHome For Your Construction Projects?
Selecting the correct slab type is not just about design; it’s about optimising cost, resources, and structural efficiency. Whether you’re working on a small residential build or a large commercial project, understanding the difference between one-way and two-way slabs can save you both time and money while improving the functionality of your construction.
At TeamHome, the best construction company in Bangalore, we don’t just build houses; we bring your dream homes to life. Known as the best construction company in Bangalore, we’re here to make the process transparent, organised, cost-effective, and fail-safe. Our team of proficient professionals simplifies your home-building process to ensure everything is engineered to perfection.
From decoding the challenges of construction to creating a home you’ll cherish for years to come, TeamHome is your partner every step of the way. Contact us today to start building your DreamHome with the confidence of a well-executed foundation.
FAQs
What is the difference between one-way and two-way slabs?
One-way slabs are supported on two opposite sides and transfer the load in one direction. Two-way slabs, on the other hand, are supported on all four sides and transfer the load in two perpendicular directions.
How to know if a slab is two-way?
A slab is considered two-way if the ratio of the longer span to the shorter span is less than or equal to 2. If the ratio is greater than 2, the slab is typically considered one-way.
What is the difference between one-way and two-way shear?
One-way shear occurs in one direction along the longer span of a slab, while two-way shear occurs in two perpendicular directions along both the longer and shorter spans of a slab.
What is a one-way slab?
A one-way slab is a type of reinforced concrete slab that is designed to primarily resist bending in one direction, typically due to its supports being located on two opposite sides.